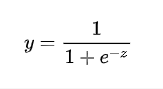使用python结合opencv占用栅格地图的实现(对数几率回归)(一)
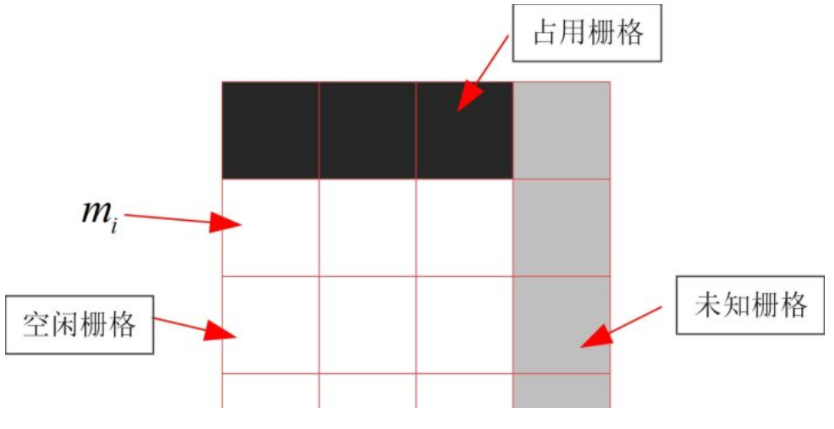
占用栅格地图occupancy grid map 是将一张图片(width * height)用一些单元的小细胞格(cell)来进行拆分,然后可以使用贝叶斯的概率公式进行 “是0非1”的估算,在小细胞格子将概率值(0-1)乘以灰度值255 实现free和 occupancy的区分。如果某一个栅格的概率是0.5以上,乘以255后将使颜色变浅变白,则认为是free状态,反之,颜色越深即黑色说明是障碍物。
相关的数学推算可以参考《概率机器人》中的mapping章节。
但是本篇文章却使用对数几率回归的模型的实现建图。也是贝叶斯滤波的概率对数形式。
该篇讲述需要理解比较困难的有:
- 对数几率的定义:如果某事件发生的概率为Px ,则反例为1-Px,两者的比值 Px/(1-Px) 为几率odds.
对其求ln ,则为 ln Px/(1-Px) 称为对数几率。英文名称log odds ,对数几率的出现是为了预测真实结果的回归。是一种学习算法。
是一种用于分类的线性回归模型。
下图的推导公式再接下来的代码中即将用到
接下来使用diy的机器车rovi进行实验,rovi车三面有三个超声波雷达,用于测距和构建实时的栅格地图使用。rovi将数据保存成data.txt然后python读取
data.txt进行测试。
senseor_modle.py
如下
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
import math
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#####################################################################################################################################
# Sonar Model
# occmap = map array, Xr = Robot X coordinate, Yr = Robot Y coordinate, Rangle = Robot heading in degrees, SonarDist = Sonar reading in mm
# thickness = Object thickness in mm, Scale = float map scale
#
# Returns: Sonar_log - Array of log odds probabilities. This can be added to existing log odds occ map to update map with latest sonar data.
# occ - Array of occupied points for scan matching
#####################################################################################################################################
def SonarModel(occmap, Xr, Yr, Rangle, SonarDist, thickness, scale):
Sonar_mask = np.zeros((occmap.shape),np.uint8)
Sonar_log = np.zeros((occmap.shape),np.single)
robotpt = (Xr,Yr)
thickness = int(thickness * scale)
SonarDist = int(SonarDist * scale)
cv2.ellipse(Sonar_mask,(int(Xr),int(Yr)),(SonarDist, SonarDist), Rangle, -15, 15, 255, -1) #Draw ellipse on to sonar mask
pixelpoints = cv2.findNonZero(Sonar_mask) #Find all pixel points in sonar cone
occ = np.empty((0,1,2),int)
for x in pixelpoints:
Ximg = x[0][0] # is a value x
Yimg = x[0][1] #
dist = np.linalg.norm(robotpt - x) #Find euclidean distance to all points in sonar cone from robot location
theta = (math.degrees(math.atan2((Yimg-Yr),(Ximg-Xr)))) - Rangle #Find angle from robot location to each cell in pixelpoints
if theta < -180: #Note:numpy and OpenCV X and Y reversed
theta = theta + 360
elif theta > 180:
theta = theta - 360
#正态分布的公式 sigma为5 位置参数u为角度theta
sigma_t = 5
A = 1 / (math.sqrt(2*math.pi*sigma_t))
C = math.pow((theta/sigma_t),2)
B = math.exp(-0.5*C)
Ptheta = A*B
Pdist = (SonarDist - dist/2)/SonarDist
P = (Pdist*2)*Ptheta
print dist,SonarDist,thickness
if dist > SonarDist - thickness and dist < SonarDist + thickness: #occupied region
Px = 0.5 + Ptheta
logPx = math.log(Px/(1-Px))
Sonar_log[Yimg][Ximg] = logPx
#print logPx
#occ = np.append(occ,[x],0)
else: #free region
Px = 0.5 - P
logPx = math.log(Px/(1-Px))
Sonar_log[Yimg][Ximg] = logPx
return Sonar_log, occ
#####################################################################################################################################
# IR Model
# occmap = map array, Xr = Robot X coordinate, Yr = Robot Y coordinate, Rangle = Sensor heading in degrees, IRDist = IR reading in mm
# thickness = Object thickness in mm, Scale = float map scale
#
# Returns: IR_log - Array of log odds probabilities. This can be added to existing log odds occ map to update map with latest sonar data.
# occ - Array of occupied points for scan matching
#####################################################################################################################################
def IRModel(occmap, Xr, Yr, Rangle, IRDist, thickness, scale):
IR_mask = np.zeros((occmap.shape),np.uint8)
IR_log = np.zeros((occmap.shape),np.single)
if IRDist == 0:
print 'IR Zero'
return IR_log
robotpt = (Xr,Yr)
IR_Max = int(600 * scale)
thickness = int(thickness * scale)
IRDist = int(IRDist * scale)
XIR = Xr + float((math.cos(math.radians(Rangle)) * IRDist))
YIR = Yr + float((math.sin(math.radians(Rangle)) * IRDist))
cv2.line(IR_mask, (int(Xr),int(Yr)), (int(XIR),int(YIR)), 255, 1)
pixelpoints = cv2.findNonZero(IR_mask) #Find all pixel points in sonar cone
occ = np.empty((0,1,2),int)
for x in pixelpoints:
Ximg = x[0][0]
Yimg = x[0][1]
dist = np.linalg.norm(robotpt - x) #Find euclidean distance to all points in sonar cone from robot location
Pdist = (IRDist - (dist/2))/IRDist
if dist > IRDist - thickness and dist < IRDist + thickness: #occupied region
if IRDist < IR_Max: #Only update occupied region if IR reading is less than maximum.
Px = 0.8
logPx = math.log(Px/(1-Px))
IR_log[Yimg][Ximg] = logPx
#occ = np.append(occ,[x],0)
else: #free region
Px = 0.3#0.5 - (Pdist/3)
logPx = math.log(Px/(1-Px))
IR_log[Yimg][Ximg] = logPx
return IR_log, occ
if __name__ == "__main__":
Xr = float(50)
Yr = float(50)
scale = float(1)/100
cv2.namedWindow("Sonar", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.resizeWindow("Sonar", 1000, 1000)
cv2.waitKey(1)
Map_log = np.full((100,100),0,np.single)
#IR_log, occ = IRModel(Map_log, Xr, Yr, -45, 590, 100, scale)
#Map_log = np.add(Map_log, IR_log)
Sonar_log, occ = SonarModel(Map_log, Xr, Yr, -90, 4500, 100, scale)
#Map_log = np.add(Map_log, Sonar_log)
Map_log =cv2.add(Map_log, Sonar_log)
#Map_P = 1 - (1/(1+(np.exp(Map_log))))
#Disp_img = 1-Map_P
Disp_img = (1/(1+(np.exp(Map_log))))
cv2.imshow("Sonar", Disp_img)
cv2.waitKey(1)
#'''
#Plot as matplotlib 3D plot
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
#plt.axis('off')
#x = np.arange(0,100,1)
#y = np.arange(0,100,1)
#X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
#ax.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Map_P)
#plt.show()
#'''
cv2.waitKey(0) #Leave window open
'''
Sonar_log = SonarModel(Map_log, Xr, Yr, -90, 6000, 100, scale)
Map_log = np.add(Map_log, Sonar_log)
Map_P = 1 - (1/(1+(np.exp(Map_log))))
Disp_img = 1-Map_P
cv2.imshow("Sonar", Disp_img)
cv2.waitKey(1)
'''
python sensormodel.py
测试效果如下图
下一篇将介绍,上面的python代码如何使用 opencv c++ 实现,研究每个函数的替代性。