occupancy grid mapping 占用栅格地图构建(三)
占用网格构图算法,主要是根据t时刻的有噪声的测量数据和机器人当前的位姿来生成连续地图。如下:
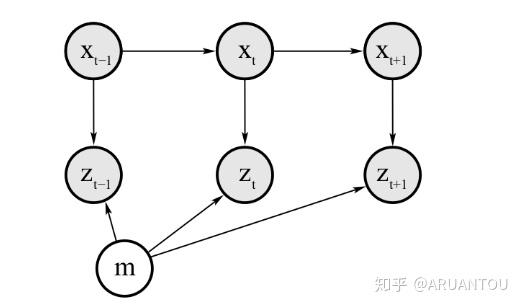
任何占用栅格建图的黄金法则都是给定数据计算地图的后验概率
我们可以发现,地图的构建就是寻找判断是否是障碍物,这样就把问题分解成为了一个二值概率的问题,讨论过这个问题的一个滤波器——二值贝叶斯滤波器binary Bayes filter。
occupancy grid mapping伪代码:
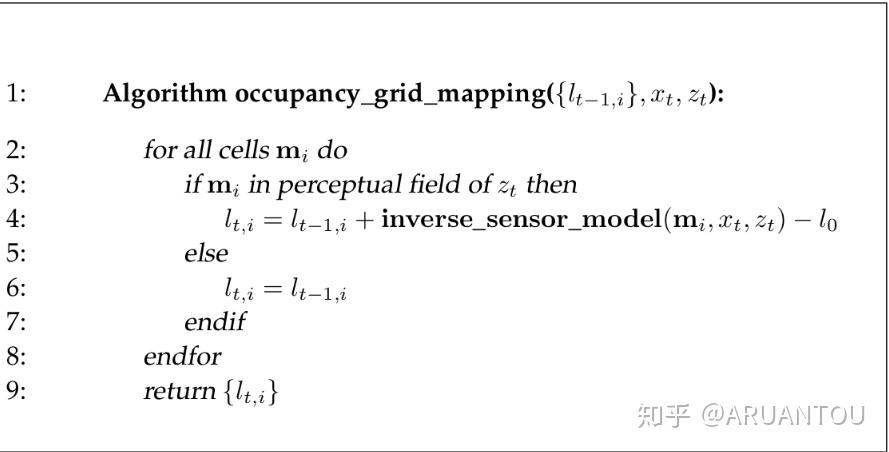
原理还是很简单的,就是遍历所有的网格,判断当前网格cell是否在传感器的扫描范围内,如果在的话,根据 和
来计算对数差异。
对数差异的逆模型的算法:

这样通过不断的获取扫描的传感器信息和机器人的位姿信息,就可以更新差异值。然后就可以计算 来获取最终的后验概率。
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Sensor characteristic: Min and Max ranges of the beams
double Zmax = 5000, Zmin = 170;
// Defining free cells(lfree), occupied cells(locc), unknown cells(l0) log odds values
double l0 = 0, locc = 0.4, lfree = -0.4;
// Grid dimensions
double gridWidth = 100, gridHeight = 100;
// Map dimensions
double mapWidth = 30000, mapHeight = 15000;
// Robot size with respect to the map
double robotXOffset = mapWidth / 5, robotYOffset = mapHeight / 3;
// Defining an l vector to store the log odds values of each cell
vector< vector<double> > l(mapWidth/gridWidth, vector<double>(mapHeight/gridHeight));
double inverseSensorModel(double x, double y, double theta, double xi, double yi, double sensorData[])
{
//******************Code the Inverse Sensor Model Algorithm**********************//
// Defining Sensor Characteristics
double Zk, thetaK, sensorTheta;
double minDelta = -1;
double alpha = 200, beta = 20;
//******************Compute r and phi**********************//
double r = sqrt(pow(xi - x, 2) + pow(yi - y, 2));
double phi = atan2(yi - y, xi - x) - theta;
//Scaling Measurement to [-90 -37.5 -22.5 -7.5 7.5 22.5 37.5 90]
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
sensorTheta = -90 * (M_PI / 180);
}
else if (i == 1) {
sensorTheta = -37.5 * (M_PI / 180);
}
else if (i == 6) {
sensorTheta = 37.5 * (M_PI / 180);
}
else if (i == 7) {
sensorTheta = 90 * (M_PI / 180);
}
else {
sensorTheta = (-37.5 + (i - 1) * 15) * (M_PI / 180);
}
if (fabs(phi - sensorTheta) < minDelta || minDelta == -1) {
Zk = sensorData[i];
thetaK = sensorTheta;
minDelta = fabs(phi - sensorTheta);
}
}
//******************Evaluate the three cases**********************//
if (r > min((double)Zmax, Zk + alpha / 2) || fabs(phi - thetaK) > beta / 2 || Zk > Zmax || Zk < Zmin) {
return l0;
}
else if (Zk < Zmax && fabs(r - Zk) < alpha / 2) {
return locc;
}
else if (r <= Zk) {
return lfree;
}
}
void occupancyGridMapping(double Robotx, double Roboty, double Robottheta, double sensorData[])
{
for (int x = 0; x < mapWidth / gridWidth; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < mapHeight / gridHeight; y++) {
double xi = x * gridWidth + gridWidth / 2 - robotXOffset;
double yi = -(y * gridHeight + gridHeight / 2) + robotYOffset;
if (sqrt(pow(xi - Robotx, 2) + pow(yi - Roboty, 2)) <= Zmax) {
l[x][y] = l[x][y] + inverseSensorModel(Robotx, Roboty, Robottheta, xi, yi, sensorData) - l0;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
double timeStamp;
double measurementData[8];
double robotX, robotY, robotTheta;
FILE* posesFile = fopen("poses.txt", "r");
FILE* measurementFile = fopen("measurement.txt", "r");
// Scanning the files and retrieving measurement and poses at each timestamp
while (fscanf(posesFile, "%lf %lf %lf %lf", &timeStamp, &robotX, &robotY, &robotTheta) != EOF) {
fscanf(measurementFile, "%lf", &timeStamp);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
fscanf(measurementFile, "%lf", &measurementData[i]);
}
occupancyGridMapping(robotX, robotY, (robotTheta / 10) * (M_PI / 180), measurementData);
}
// Displaying the map
for (int x = 0; x < mapWidth / gridWidth; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < mapHeight / gridHeight; y++) {
cout << l[x][y] << " ";
}
}
return 0;
}
github:
https://github.com/horo2016/Occupancy-Grid-Mapping-Algorithm