breezyslam建图2d-slam建图测试一
这篇文章是基于breezyslam 建图的后续,对breezyslam的建图进行测试,
使用树莓派3B+思兰激光雷达,
使用Python的所有库,所有库的安装和记录请查看这篇文章
教程四:树莓派搭建breezyslam环境的说明
http://blog.cvosrobot.com/?post=486
笔者编写了下面的脚本
#!/usr/bin/env python3
'''
rpslam_vos.py : BreezySLAM Python with SLAMTECH RP A1 Lidar
Copyright (C) 2018 Simon D. Levy
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
along with this code. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
'''
MAP_SIZE_PIXELS = 500
MAP_SIZE_METERS = 10
LIDAR_DEVICE = '/dev/rplidar'
# Ideally we could use all 250 or so samples that the RPLidar delivers in one
# scan, but on slower computers you'll get an empty map and unchanging position
# at that rate.
MIN_SAMPLES = 180
import sys
import os
import time
from breezyslam.algorithms import RMHC_SLAM
from breezyslam.sensors import RPLidarA1 as LaserModel
from rplidar import RPLidar as Lidar
from roboviz import MapVisualizer
from rplidar import RPLidarException
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Connect to Lidar unit until lidar is normal
berror = True
while berror == True:
lidar = Lidar(LIDAR_DEVICE)
try:
info = lidar.get_info()
berror = False
except RPLidarException as err:
print(err)
time.sleep(1)
berror = True
lidar.stop()
lidar.disconnect()
pass
# print lidar information
print(info)
#print lidar health status
health = lidar.get_health()
print("health status:")
print(health)
# Create an RMHC SLAM object with a laser model and optional robot model
slam = RMHC_SLAM(LaserModel(), MAP_SIZE_PIXELS, MAP_SIZE_METERS)
# Set up a SLAM display
viz = MapVisualizer(MAP_SIZE_PIXELS, MAP_SIZE_METERS, 'VosSLAM')
# Initialize an empty trajectory
trajectory = []
# Initialize empty map
mapbytes = bytearray(MAP_SIZE_PIXELS * MAP_SIZE_PIXELS)
# Create an iterator to collect scan data from the RPLidar
# iterator = lidar.iter_scans()
# We will use these to store previous scan in case current scan is inadequate
previous_distances = None
previous_angles = None
# First scan is crap, so ignore it
# next(iterator)
while True:
for i,scan in enumerate(lidar.iter_scans()):
print('%d: Got %d measurments' % (i, len(scan)))
if i > 0:
distances = [item[2] for item in scan]
angles = [item[1] for item in scan]
# Update SLAM with current Lidar scan and scan angles if adequate
slam.update(distances, scan_angles_degrees=angles)
# Get current robot position
x, y, theta = slam.getpos()
# Get current map bytes as grayscale
slam.getmap(mapbytes)
# Display map and robot pose, exiting gracefully if user closes it
if not viz.display(x/1000., y/1000., theta, mapbytes):
exit(0)
# Extract distances and angles from triples
# Shut down the lidar connection
lidar.stop()
lidar.disconnect()
python3 rpslam_vos.py
Incorrect descriptor starting bytes
{'model': 24, 'hardware': 0, 'firmware': (1, 18), 'serialnumber': '5CB4FBF2C8E49CCFC6E49FF1A266530D'}
health status:
('Good', 0)
0: Got 140 measurments
1: Got 210 measurments
2: Got 208 measurments
3: Got 207 measurments
4: Got 213 measurments
5: Got 212 measurments
6: Got 212 measurments
7: Got 213 measurments
8: Got 207 measurments
9: Got 214 measurments
10: Got 218 measurments
11: Got 214 measurments
12: Got 211 measurments
13: Got 209 measurments
14: Got 214 measurments
15: Got 215 measurments
16: Got 210 measurments
17: Got 211 measurments
18: Got 214 measurments
19: Got 214 measurments
20: Got 212 measurments
21: Got 214 measurments
22: Got 206 measurments
23: Got 215 measurments
24: Got 216 measurments
25: Got 211 measurments
26: Got 213 measurments
27: Got 209 measurments
28: Got 211 measurments
29: Got 208 measurments
30: Got 206 measurments
31: Got 215 measurments
32: Got 207 measurments
33: Got 205 measurments
34: Got 215 measurments
在测试过程发现,思兰的激光雷达供电不足导致读取数据失败。所以树莓派的供电一定要足。
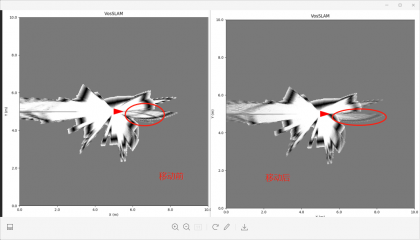
下图是测试场景。
从图中可以看到基本是没有变化,可以看出 没怎么变化,所以怀疑还是得用到odom 或者预估odom的开关没打开。
待看下次测试。





最新评论
x_mm, y_mm, theta_degrees = slam.getpos()
# Add new position to trajectory
trajectory.append((x_mm, y_mm))